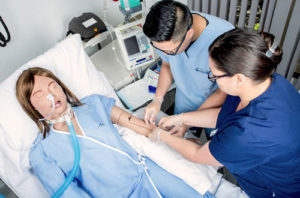
Healthcare simulation is the modern way to educate and train healthcare professionals to master cognitive, technical, and behavioral skill sets through technologically advanced crafted experiences. The term healthcare simulation is also commonly referred to as medical simulation or, in specific circumstances, surgical simulation and nursing simulation.
How does the healthcare simulation methodology work? The process begins in a fully immersive scenario where a manikin typically acts as the patient. Usually, moulage medical makeup (such as a burn wound) is applied to the medical simulator to provide for the most realistic patient presentation. While being wirelessly controlled by a healthcare simulation educator during the experiential scenario, the learner (student or professional) is expected to perform all necessary practices or procedures on the patient simulator.
The scenario participants then manipulate the human patient simulator and their healthcare environment, and the actions and results are digitally streamed live to other learners through audiovisual debriefing systems. The purpose of this video stream is also so that a recording is available for playback during the clinical simulation debriefing process. The ability to recap performances is vital to the overall learning process, as this analytical conversation helps to equally address errors and highlight success.
Debriefing is where the real learning takes place. This unique process is best accomplished when clinical faculty are trained to step back and prompt the learners to discuss what they experienced or witnessed through the recording system, as opposed to using simulation as just another excuse to lecture.
Healthcare simulation learning experiences have the opportunity to be customized to address the needs of the learner for professionals. Thus, healthcare simulation can accommodate a wide range of learners. They can range from beginner-level learners looking to build “muscle memory” to expert professionals who are required to master a new technology or piece of equipment needed for a complex procedure.
Adding to the scenarios’ realism, fidelity in simulation is the level of realism portrayed in a simulated educational or training experience. Fidelity is the route of the Latin word fidelitas, meaning the exactness of the degree to which something is copied or reproduced. In the context of healthcare simulation, fidelity represents how accurate a clinical learning experience is to real-world patient care. In the most basic terms, a low-fidelity simulation is less realistic than a high-fidelity simulation. A high-fidelity healthcare simulation is any scenario that reproduces an actual patient scenario to a high level of realism inclusive of physical, environmental, psychological, and other components.
The level of realism continues to increase throughout the global medical simulation industry, in part because the costs of new technologies continue to decrease. One day patient simulators will be so realistic that clinical students won’t know they are talking to a manikin or virtual patient.
Virtual simulation during COVID-19
During the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, many simulation centers and facilities were forced to temporarily shut their doors. This led to seeking alternative methods to relay healthcare simulation scenarios to learners. As a result, many clinical simulation centers sought ways to take their simulations online, providing learners with access from anytime and anywhere. Given the coronavirus pandemic, this convenience and flexibility has become crucial to reaching optimal learning outcomes.
Now, online or hybrid curricula can include healthcare simulation scenarios, observations, and assessments. They can also help learners with the accrual of requisite clinical examination hours. Further, virtual simulation technology has the ability to help learners better prepare for boards and high-stakes exams.
During COVID-19 the demand for remote-based learning systems including telesimulation, virtual reality, augmented reality, and desktop-based learning has exploded. With clinical rotations cancelled and campuses closed, educators were forced to consider emerging technologies to fill the gaps.
One way virtual simulation works is by enabling the learner to conduct high-impact standardized patient encounters and simulation sessions in a fully online environment. Plus, a virtual technology platform’s integrated telemedicine training features can help educators bridge the gap to modernized healthcare simulation environments, as well as meet the critical need to practice shifting clinical treatment in telemedicine formats.
Virtual simulation technology can also help healthcare simulation educators to streamline the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, and delivery of their in-person or online educational courses and training programs. This is made possible while allowing them to safely and securely maintain their videos, livestreams and recordings, and student data. Educators can feel confident knowing that the full scope of their online and video-based clinical training delivery is safe with enhanced password protection and data encryption.
A virtual simulation platform further helps educators establish a seamless online alternative to in-person training, providing the flexibility to shift learning along with the needs of their learners—all while maximizing engagement and outcomes. With integrated, intuitive virtual simulation workflows, they can also observe and provide quality control for the educational experience across multiple locations.
The clinical training world may never return to what it was before COVID-19; in all likelihood, distance and hybrid learning is here to stay. This means that healthcare simulation is more important than ever to maximizing educational outcomes.
- A bungled FAFSA rollout threatens students’ college ambitions - April 19, 2024
- Using real-world tools to prepare students for the workforce - April 18, 2024
- 8 top trends in higher education to watch in 2024 - April 16, 2024